Python (Chapter 5.1) : Operations "OF" LIST
For any type of consultation, query or doubt. You may contact to the following: (+91) 9804 436 193 debabrataguha20@gmail.com
and join the group https://www.facebook.com/groups/331231161093613/
Operations of List
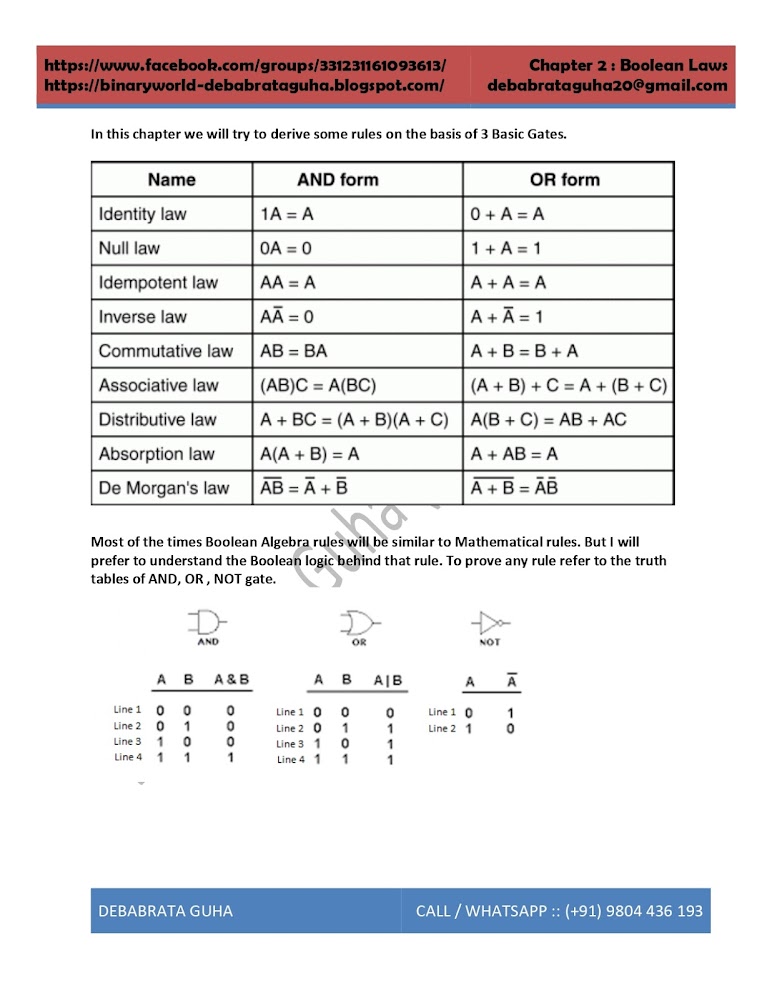
We will discuss all the properties of List here. List has all the below methods defined in it. I will suggest to type and execute these codes in your python interpreter as well. I am repeating myself that ALL the methods of LIST are mentioned below. So once we finish this chapter, LIST will be much simpler for you. But you have to execute these 1-2 lines of code in your python interpreter simultaneously.
1. To declare a list named students
students=["William","Shreya","David","Amol"]
2. To print a list
print (students)
output:
['William', 'Shreya', 'David', 'Amol']
3. To
print the datatype of studentsprint (type (students))
output:
<class ‘list’>
4. To print the length of the list
print (len(students))
output:
4
5. To print the name of 1st student
print (students[0])
output:
'William'
6. To print the name of 2nd student
print (students[1])
output:
'Shreya'
7. To print the name of last student
print (students[-1])
output:
'Amol'
8. To print the name of 2nd last student
print (students[-2])
output:
'David'
9. To print the last element by the length of list
print (students[len(students)-1])
output:
'Amol'
10. To print the 1st 2 elements
print (students[0:2])
output:
['Williams', 'Shreya']
11. To print the 2nd and 3rd elements means the elements at position 1 and 2
print (students[1:3])
output:
['Shreya' , 'David']
12. To print the length of the part of list
print (len(students[1:]))
output:
3
13. To print the elements starting from zero, we can skip the initial zero.
print (students[:3])
output:
['Williams', 'Shreya' , 'David']
14. To print the elements starting from zero and print every 2nd element , bring a third argument as 2
print (students[:3:2])
output:
['Williams', 'David']
15. To print the elements starting from zero and print every 2nd element till last , we can skip the middle argument
print (students[::2])
output:
['Williams', 'David']
16. To
print the list after slicing the last 2 elements from back. (remember, slicing
the elements from position -1,-2)
print (students[:-2])
output:
[ 'Williams' , 'Shreya' ]
17. To print a range of list after calculating elements from back.(-3:-1 means elements at -3 and -2)
print (students[-3:-1])
output:
[ 'Shreya' , 'David' ]
print (students[::-1])
output:
[ 'Amol' , 'David' , 'Shreya',
'Williams']
print (students[::-2])
output:
[ 'Amol' , 'Shreya' ]
students.append("Irfan")
print (students[:])
output:
['Williams', 'Shreya', 'David'
, 'Amol' , 'Irfan' ]
21. To insert an element at 2nd position or position 3
students.insert(3,"Roy")
print (students)
output:
['Williams', 'Shreya', 'David'
, 'Roy', 'Amol' , 'Irfan' ]
22. To insert multiple element at the last of list
students.extend(["Robert","James","Antenio"])
print (students)
output:
['Williams','Shreya','David','Roy','Amol','Irfan','Robert','James','Antenio']
23. To remove by position, here we are deleting 5th element
Students.remove(5)
print (students)
output:
['Williams','Shreya','David','Roy','Amol','Robert','James','Antenio']
24. To remove by value, here we are deleting Robert
Students.remove("Robert")
print (students)
output:
['Williams','Shreya','David','Roy','Amol','James','Antenio']
print (Students.pop(3))
print (students)
output:
'David'
['Williams','Shreya','Roy','Amol','James','Antenio']
print (Students.pop())
print (students)
output:
'Antenio'
['Williams','Shreya','Roy','Amol','James']
print (Students.count("Roy"))
output:
1
print (Students.index("Amol"))
output:
3
students.reverse()
print (students)
output:
['James',
'Amol' , 'Roy' ,'Shreya' ,'Williams']
st1=students.copy()
print(st1)
output:
['James',
'Amol' , 'Roy' ,'Shreya' ,'Williams']
students.sort()
print (students)
output:
['Amol'
, 'James', 'Roy' ,'Shreya' ,'Williams'] Even we can sort the list in descending order as well.
students.sort( reverse=true )
print (students)
output:
[ 'Williams' ,'Shreya' ,'Roy' ,'James','Amol'
,]
students.clear()
print (students)
output:
[] 33. We can create list with elements having different datatype.
S1=[1,"Hi",3.5,"Hello"]
print (S1)
output:
[1,'Hi',3.5,
'Hello']34. We can create a new list even with a another list datatype.
S2=[ 2, ["Raj","Alok"]
, ["Bibek"]]
print (S2)
output:
[2, ['Raj', 'Alok'], ['Bibek']]
35. Print the element inside the sublist.
print (S2[1][0])
output:
Raj
36. Append S2 as a new list element at the end of S1
S1.append(S2)
print(S1)
output:
[1, 'Hi', 3.5, 'Hello', [2, ['Raj', 'Alok'], ['Bibek']]]

Comments
Post a Comment